Does birth control make you gain weight? Cause infertility? Help with acne? Issues of birth control, pregnancy, and fertility are critically important to many adults but there are many rumors and rumors and misinformation to contend with.
To help separate fact from fiction, we are taking a look at the myths surrounding birth control and its effect on fertility and other issues. Read on for a comprehensive look at types of birth control, their effects, and their rates of effectiveness.
Effectiveness of Birth Control Types
Currently, there are more than a dozen recognized forms of birth control with effectiveness rates ranging from 71% effective to 99% effective. Here we will take a brief look at each.
99% Effective Birth Control Methods
Arm Implant: An arm implant is among the most effective and longest lasting birth control methods. This hormone-based implant is inserted into your arm by your doctor and will continue to release pregnancy-preventing progestin for up to 5 years or until your doctor removes it.
Pros: Arm implants are highly effective, long-lasting, low maintenance and can decrease cramps associated with menstruation. Also, unlike oral contraceptives, you do not risk forgetting to take your birth control.
Cons: Serious complications from implants are rare but some patients may experience infections at the site of insertion, headaches, and bleeding. You should also be aware that there is a chance that the implant may move. If you no longer can feel your implant in your arm, contact your doctor immediately to determine if the implant has moved and needs to be extracted.
Hormonal IUD: A hormonal IUD is a small, plastic T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus by your doctor. This, like the arm implant, also releases the hormone progestin. Progestin prevents eggs from being released from the ovaries. Therefore, they cannot be fertilized.
Pros: Unlike the arm implant, you will not feel the hormonal IUD once it is in place. Though there are small strings that protrude slightly from the cervix, neither you nor your partner will feel these. This style of IUD can last up to 7 years.
Cons: The most common side effects of a hormonal IUD are cramps and backache for the first few days after the device is inserted. You may also notice light vaginal spotting between periods for the first several months after insertion. Rarely, complications may arise from an infection or if the IUD pokes through the uterine wall.
Copper IUD: The copper IUD is very similar to the hormonal IUD in that it is inserted in the same way and has the same risks and benefits. However, it has the advantage over a hormonal IUD in two ways:
- Longest lasting birth control with up to 12 years of protection.
- It is the only 99% effective birth control that does not contain hormones.
Birth Control Shot: The birth control shot contains the hormone progestin and is administered by your healthcare provider every three months.
Pros: Unlike IUDs that are inserted, there is no risk of a device moving and causing problems. Instead, the shot is quickly administered every three months for 99% effective birth control with minimal side effects.
Cons: With a shot, you may notice increased mood swings, weight gain, acne, and soreness in your breasts. However, one of the biggest risks associated with the shot is that patients often fail to get their dosage on time. When you delay getting your dosage, the effectiveness of the shot drops to 94%.
Vasectomy/Tubal Ligation: Vasectomy (for men) and Tubal Ligation (for women) are surgical, permanent birth control forms. Each is considered 99% effective. Complications and risks are rare with both procedures but Tubal Ligation is more invasive. Technically, both procedures can be reversed but it can be a complicated procedure that is not guaranteed to restore fertility.
91% Effective Birth Control Methods
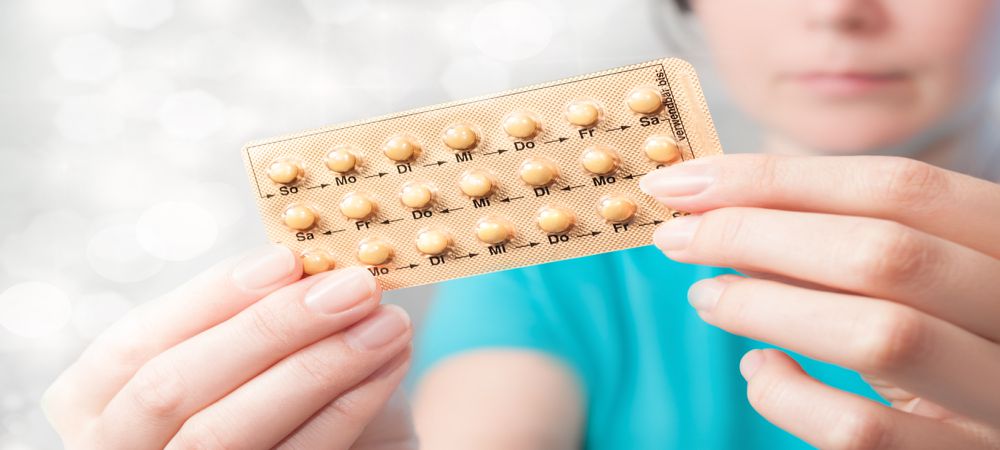
Birth Control Pill: Birth control pills cover a wide range of brands and varieties of oral contraceptives but all work similarly. With this method, you take a pill each day which releases estrogen and progestin. Since there are multiple types and brands, side effects can vary. Users commonly report headaches, mood swings, decreased sex drive, and spotting between periods. In some cases, blood clots can form but this is rare.
Pros: A pill does not require you to visit your doctor every three months the way the shot does. If you have acne, the pill can help to reduce this along with pain during menstruation. You can also attempt to get pregnant as soon as you stop taking the pill.
Cons: The pill can affect your mood, decrease sexual interest, cause headaches and bloating. Forgetting to take your pill daily will increase the likelihood of you getting pregnant.
Note: There is also a “minipill” which contains a lower dose of hormones. Your doctor will be able to tell you if this option is right for you.
Vaginal Ring: The vaginal ring is a soft, flexible ring that is inserted into the vagina for three weeks out of the month. It also uses hormones to prevent pregnancy. On the fourth week of the month, you remove the ring to have your period naturally.
Pros: Like the pill, the ring will help to reduce acne and body hair. It is also comfortable for most patients and your partner will not be able to feel it during intercourse.
Cons: Blood clots may occur though this is rare. Those who smoke and/or who have high blood pressure will increase their risk of this complication. The ring’s effectiveness is also reduced when not used properly, i.e. not removed or replaced when required.
71% to 88% Effective Methods
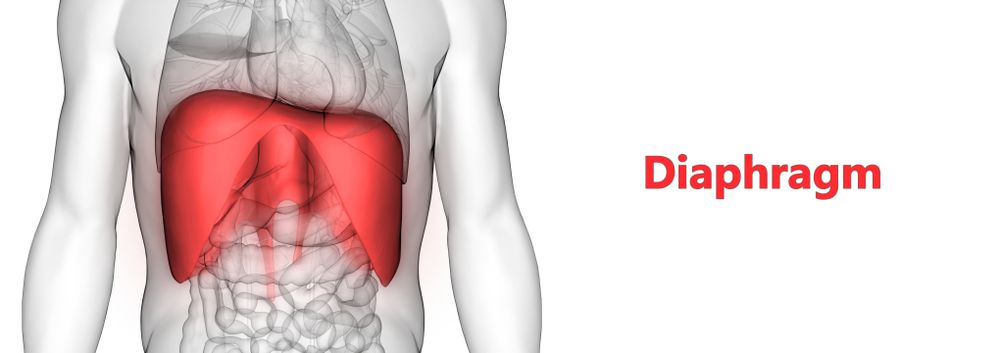
- 88% Effective Diaphragm: A diaphragm is a small silicone cup that fits over the cervix. It is placed just before sex and prevents sperm from entering. The diaphragm is beneficial in that it does not contain hormones or side effects. However, fitting the device correctly can be difficult which reduces its rate of effectiveness.
- 71% Effective Spermicide: Spermicide is a cream that kills sperm. To optimize the effectiveness of this cream, it should be combined with condoms and/or a diaphragm. When used on its own, it can be difficult to get adequate protection.
- 85% Effective Condoms: perhaps the most common form of birth control, condoms are a thin sheath of latex placed over the penis before sex. While they are the only birth control that is effective in preventing STDs, they are not the most effective at preventing pregnancy. Optimally, combine condoms with another form of birth control to get the best protection from both STDs and pregnancy.
- Natural Methods: Natural methods of birth control involve tracking fertility days. While this can be up to 88% effective when done perfectly, it is not a perfect system. Those with irregular menstruation cycles should not use this as their only form of birth control.
Quick Facts About Birth Control
- Condoms are the only birth control that reduces the chances of contracting a sexually transmitted disease.
- A copper IUD is the only 99% effective form of birth control that does not contain hormones.
- The only permanent form of birth control is tubal ligation and vasectomy.
- Some forms of birth control, such as the vaginal ring, can increase the risk of blood clots. This is especially dangerous for those with unmanaged blood pressure and for those who smoke.
- Using other forms of birth control such as the pill or vaginal ring along with condoms can provide better protection from both pregnancy and STDs.
- The pill and the vaginal ring can both reduce acne and body hair.
Does Birth Control Cause Infertility?
It is a common myth that the birth control pill will cause infertility. However, there is no truth to this. As with all of the previously mentioned birth control methods (with the exception of tubal ligation and vasectomy), you can cease use and begin trying to get pregnant immediately.
How Long Should it Take to Get Pregnant?
It is a common trope in pop culture that women will get pregnant almost immediately. Because of this, many women attempting to get pregnant feel there is something wrong if they do not conceive within a month or two. However, while pregnancy can happen this quickly, it is just as common for it to take several months or even a year of regular attempts.
As a general rule, women under the age of 35 should not be concerned about infertility until they have attempted to get pregnant for a year or more. Women 35 to 40 can continue to attempt getting pregnant for up to 6 months before seeing a doctor about fertility issues. However, those who are over 40 should seek medical guidance from the start. Tests can show your likelihood of conceiving naturally and fertility treatments can be administered as needed.
Final Thoughts on Birth Control and Fertility
Infertility is a common issue and there are many reasons for it. However, birth control is not one of them. If you are concerned about your ability to get pregnant, speak with your doctor. There are several modern treatments and solutions to help increase the probability of conceiving.
At BCML, our caring medical professionals are here to guide you through all your health concerns including birth control and fertility. To schedule a consultation, contact us at 416-921-2121 & 1-800-667-0923 (toll free #).